
The corresponding area in an animal can also be referred to as the chest. In the human body, the region of the thorax between the neck and diaphragm in the front of the body is called the chest. Arteries and veins are also contained – ( aorta, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and the pulmonary artery) bones (the shoulder socket containing the upper part of the humerus, the scapula, sternum, thoracic portion of the spine, collarbone, and the rib cage and floating ribs).Įxternal structures are the skin and nipples. The contents of the thorax include the heart and lungs (and the thymus gland) the major and minor pectoral muscles, trapezius muscles, and neck muscle and internal structures such as the diaphragm, the esophagus, the trachea, and a part of the sternum known as the xiphoid process. Main article: Thoracic cavity An X-ray of a human chest area, with some structures labeled
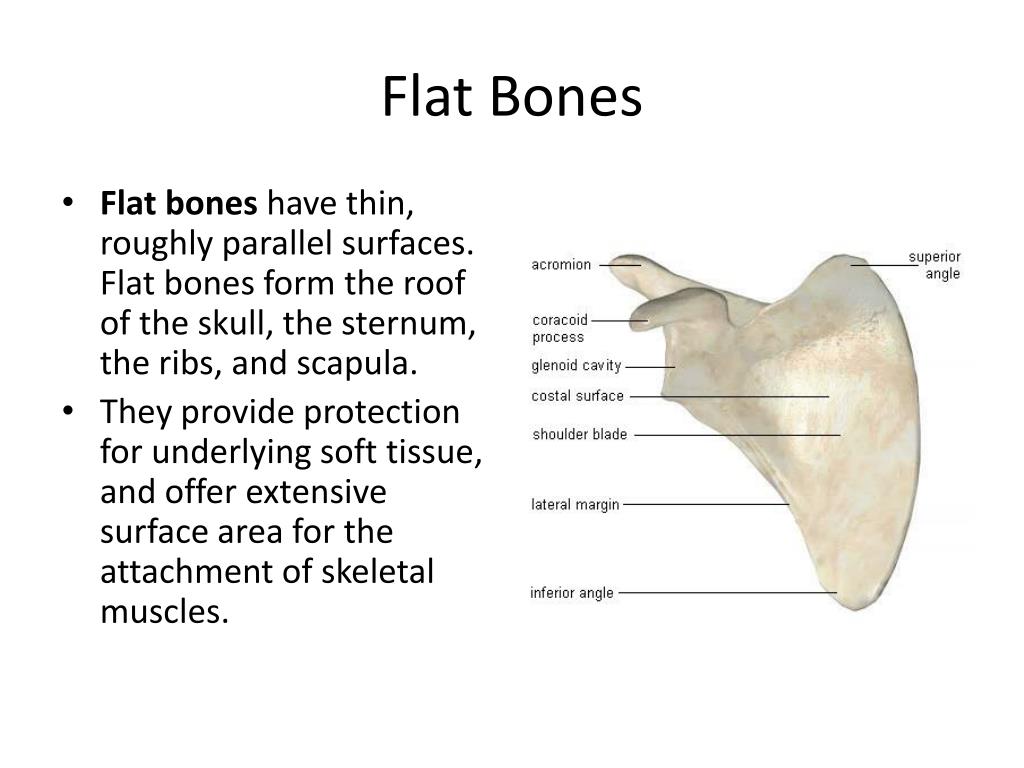
It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, and shoulder girdle. In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ thorax " breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via Latin: thorax. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain.Īdolescent male chest and nipples. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures.
The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments.

The thorax ( PL: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
